
一种用于3D细胞培养的功能化微凝胶棒交联形成的软大孔结构。
Introduction
思路:
- 为了了解生命物质和人造材料之间的相互作用,组织工程研究小组专注于开发具有越来越可控特性的3D支架:
- 软水凝胶支架通常通过交联前体溶液形成,从而产生柔软的组织模拟结构。细胞在交联之前被封装在前体中,而形成的水凝胶允许细胞通过降解和/或重塑网络来扩散和增殖;
- 大孔3D支架是通过静电纺丝、溶剂浇铸或气体发泡/颗粒浸出等多种技术制造的,其优点是细胞迁移和增殖不需要降解,从而提高了细胞浸润率。
- 与大块水凝胶或刚性支架相比,开发具有微米级孔隙的软环境,能增强细胞侵袭和迁移,同时有助于形成3D功能组织和组织修复。
- 球形微凝胶通过共价或物理粉碎方式形成多孔支架,但前者缺乏稳定3D结构,后者孔隙率控制困难;
- 棒状和更复杂形状的微凝胶,可以获得更大的孔隙率,但必须由周围的容器维持,直到细胞增殖和附着而发生足够的互连以稳定支架;
- 液滴微流控系统可产生微凝胶棒,但因为它们主要形成堆叠结构,导致棒之间的大孔率较低。
- 大孔材料对于3D细胞培养十分必要,然而迄今为止,尚未报道具有孔径范围为≈50—200 µm的基于微凝胶棒自交联形成的大孔微凝胶支架。
- 作者提出一种通过自组装和快速互连两种带有互补反应基团的棒状微凝胶来创建稳定的微米到毫米级的大孔结构。该方法可以使用不等轴微凝胶尺寸和纵横比来多样化和增强对微孔退火粒子(Microporous annealed particle,MAP)支架孔隙率的控制,同时可以独立改变生化和机械性能。
- 与基于球形微凝胶的支架相比,孔径由球体的直径决定,而相同的棒状微凝胶体积有可能产生更大的孔。
Microgel Rod Production via Continuous Plug-Flow On-Chip Gelation
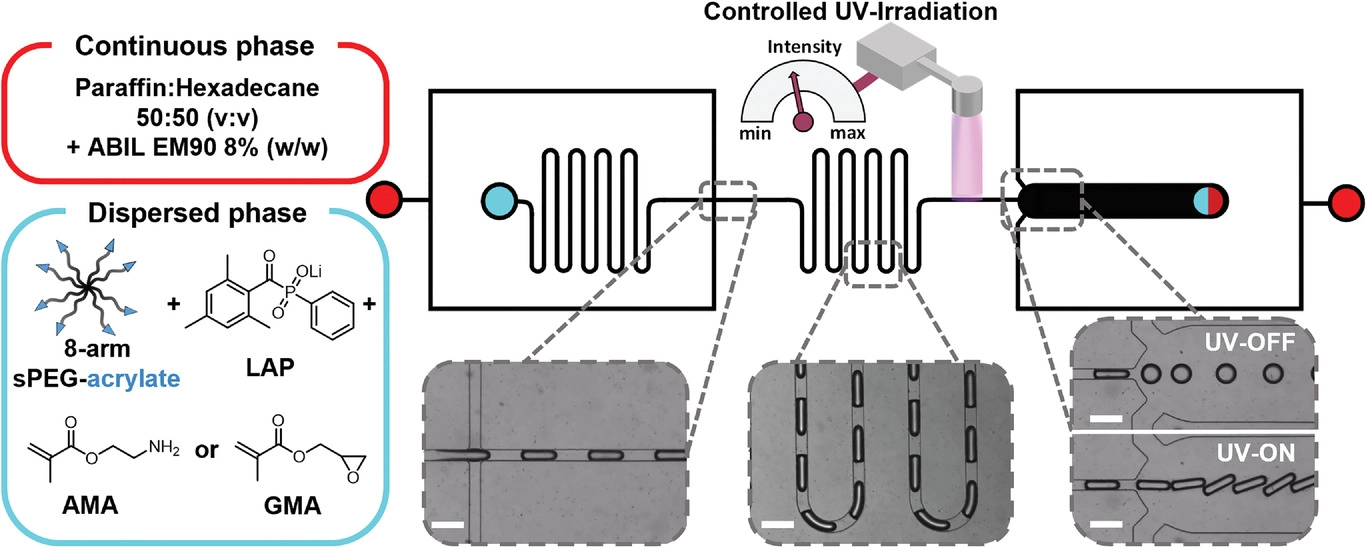
微流控芯片设计和设置。通过活塞流状态下的光引发,连续生产功能化微凝胶棒。红色表示第一和第二连续油相(多聚甲醛+十六烷+ABIL EM90)的入口,青色表示分散水相(sPEG-AC+LAP+AMA/GMA)的入口。输出标记为半红半青。虚线插入显示在操作过程中拍摄的特征部分的白光图。通过光引发自由基聚合产生微凝胶棒,生产速度约为每小时11300个微凝胶。
AMA:制造伯胺功能化微凝胶;
GMA:制造环氧功能化微凝胶。
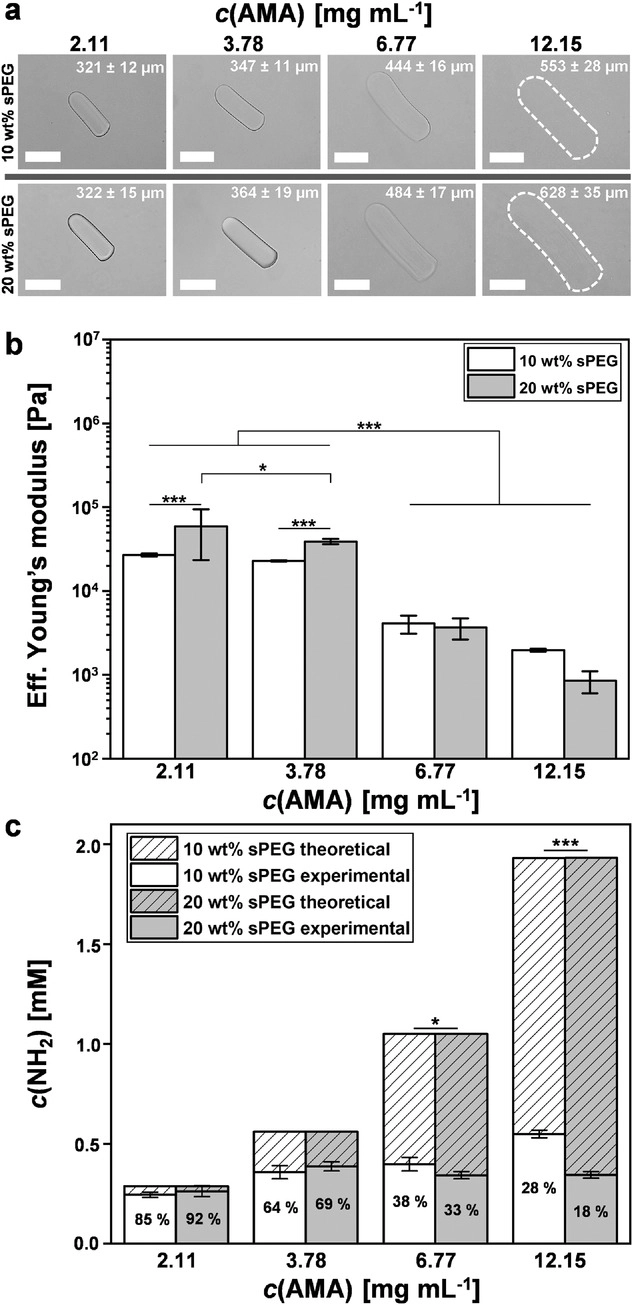
- (a)不同AMA浓度微凝胶棒在水中的白光图,较高的AMA浓度显著增加了微凝胶的膨胀,这可能与微凝胶网络内亲水性伯胺的密度增加有关。比例尺:200μm。
- (b)PBS中AMA微凝胶棒的杨氏模量。交联密度和膨胀度之间呈反相关,在低AMA浓度下,当PEG浓度加倍时,微凝胶略微变硬。
- (c)通过茚三酮测定对AMA微凝胶棒的胺掺入定量,随着AMA浓度增加而增加。由于微凝胶的膨胀行为与检测到的不同AMA浓度的伯胺相比变化更大,因此微凝胶棒机械性能变化的原因似乎更可能与芯片上凝胶的差异有关。
Microgel Assembly and Interlinking Studies

- (a)将用不同的AMA浓度合成的胺功能化微凝胶棒与环氧功能化微凝胶棒混合。使用高AMA浓度的胺功能化微凝胶棒时观察到成功的互连,而AMA浓度较低的微凝胶棒无法与其环氧对应物有效互连。
- (b)在每个微凝胶棒的中间高度拍摄的荧光FITC信号的激光共聚焦扫描显微镜图像与相应的白光图叠加,表现不同AMA浓度的胺分布(青色FITC信号描绘伯胺分布),虚线轮廓表示微凝胶棒边缘。发现较低的AMA浓度下,在微凝胶的外侧观察到胺不足的非荧光PEG层,这可能抑制与环氧官能化微凝胶的互连。

- (a)由环氧功能化微凝胶棒(红色)与相同数量的胺功能化微凝胶棒(青色)混合而成的相互连接的支架的共聚焦三维投影。
- (b)不同的Z值(插图)焦点上的Z-堆叠图像,代表了相互连接的支架内的多孔结构。
- (c)在镊子(I)和所采用的微流控芯片上(II)的相互连接的微凝胶棒支架的图像。
DWI:弥散加权成像,利用水分子的状态来成像。

- (a)具有不同纵横比的环氧功能化微凝胶棒的共聚焦图像(红色)。
- (b)不同长宽比的环氧功能化微凝胶棒与胺功能化微凝胶棒的相互连接形成的支架的共聚焦Z型堆叠图像。
- (c)在水(左)和RPMI+细胞培养基(右)中的微凝胶支架的膨胀特性成像。两种类型的微凝胶在细胞培养基中塌陷而不破坏相互连接的支架结构。
- (d)上述支架在水和培养基中的Z堆叠的量化。三个纵横比都会产生稳定的互连支架。
L929 Cell Studies on Individual Microgel Rods

- (a)在t = 0和120 min的实时成像期间显示细L929小鼠成纤维细胞附着的白光图。白色箭头表示细胞-材料相互作用的丝状伪足状突起。
- (b)L929细胞在不同微凝胶表面上的附着效率的量化。可以看到,有较高胺浓度时细胞更容易附着。更高浓度的sPEG-AC细胞附着更圆,即不够舒展。环氧功能化微凝胶仅当使用GRGDS-PC后修饰后才有细胞附着。
- (c)荧光共聚焦图像显示培养4 d后单个微凝胶棒上的细胞扩散和生长。微凝胶轮廓用白色虚线表示,肌动蛋白为黄色,细胞核为蓝色。具有最高AMA浓度的10 wt% sPEG微凝胶表现出最多的扩散细胞数量。在培养过程中,成纤维细胞增殖并几乎覆盖整个微凝胶表面。同时,对于20 wt% sPEG微凝胶,细胞在微凝胶表面形成簇状组装,表明细胞-微凝胶相互作用减少。
GRGDS-PC:活性多肽,用于促细胞粘附。
L929 Cell Culture inside Interlinked Macroporous 3D Scaffolds

- (a)在大孔支架内培养4 d和7 d后,L929细胞的250 µm共聚焦Z堆叠的3D表示。胺功能化微凝胶在芯片上交联过程中用GRGDS-PC进行改性,环氧功能化微凝胶用GRGDS-PC进行后改性,以 免干扰环氧基团。可以见:在没有对环氧功能化微凝胶进行后修饰时,细胞网络连续性降低,以其细胞仅附着在具有GRGDS-PC的胺功能化微凝胶上(没有附着细胞的微凝胶棒以虚线轮廓表示)。使用GRGDS-PC后修饰的环氧微凝胶棒构成的支架上能观察到更多相互连接的细胞结构。
- (b)Z堆叠的细胞体积量化。比较了有无GRGDS-PC对环氧官能化微凝胶进行后修饰的情况下细胞随时间的生长状况。
- (c)支架内培养的第7 d时相连细胞结构,其中微凝胶用GRGDS-PC进行了后修饰,虚线轮廓表示微凝胶棒。
- I和II:共聚焦显微图像显示覆盖和桥接相邻微凝胶棒的细胞结构;
- III:共聚焦显微图像显示在不同高度的大孔中形成的桥接细胞结构;
- IV:共聚焦显微图像显示由两个单元形成的桥接结构,总之显示出支架内明显的细胞相互作用。
Human Fibroblast and Endothelial Cell Culture Studies

- (a)在加入HUVEC和额外的成纤维细胞(1:3)之前,在微凝胶棒支架内培养5 d的人成纤维细胞并再培养14 d。
- (b)在加入HUVEC和额外的成纤维细胞(1:3)之前,在微凝胶棒支架内培养7 d的人成纤维细胞并再培养16 d 。
- (c)同一支架的边缘附近的Z叠加3D图。其中,黄色表示肌动蛋白,蓝色表示细胞核,洋红色表示CD-31/PECAM-1标记的HUVEC。可以看到部分内皮细胞的生长和扩散。
Discussion
- GRGDS-PC肽修饰微凝胶,使其具有细胞粘附性。虽然胺官能化微凝胶可以在芯片上进行改性,但环氧微凝胶在组装和互连 3D 结构后进行后改性,以防止干扰反应性环氧基团。
- 结合实时成像分析以探测L929细胞在单个GRGDS-PC修饰的微凝胶棒上的附着和扩散,固定和染色培养物的共聚焦显微镜表明,相互连接的支架具有很强的细胞粘附性并支持培养中沿微凝胶表面的细胞生长
- 细胞在组装的微凝胶结构中增殖和迁移,并在培养期间填充支架孔,而细胞具有形成跨孔桥接多个微凝胶的结构的能力。
- 天然纤连蛋白的产生支持内皮细胞发芽和血管形成。由于在微凝胶棒和细胞之间的界面以及存在于大孔中的细胞之间的相互连接的微凝胶棒基支架内的细胞培养后观察到天然纤连蛋白,因此预计它会促进内皮细胞的组织血管化。
Conclusion
提出一种用于3D细胞培养的功能化微凝胶棒交联形成的软大孔结构,以在体外培养3D组织以进行药物和治疗测试。特别的,它们可能有利于血管向生长组织内生长,以提供营养和氧气。
Reference
Rommel D, Mork M, Vedaraman S, et al. Functionalized Microgel Rods Interlinked into Soft Macroporous Structures for 3D Cell Culture[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, n/a(n/a): 2103554.



